Industrial Zoning: Benefits and Potential Risks
Industrial zoning is the blueprint for the physical structures of towns and cities. It regulates the areas where businesses and properties are allowed to operate, ensuring that their ecological and community impacts are thoroughly observed.Any entrepreneur or developer who wishes to collaborate with the warehousing, distribution, and manufacturing sectors should be familiar with the fundamentals of industrial zoning. These areas are often subjected to unique restrictions to regulate noise, pollution, and construction activities. Hence, knowing the ins and outs is significant as it could mean the difference between costly legal challenges and smooth operation.
Even though it may initially seem intimidating, navigating its complexities doesn’t have to be frightening. Furthermore, it is crucial to understand the permitted uses, potential restrictions, and the thorough process for requesting modifications, if any. Specific rules and laws are applied in various jurisdictions that regulate how the land is used and what kind of authorities are required to operate.Anyone hoping to expand or launch their industrial businesses or properties has to be aware of these. Want to learn more about industrial zoning? Keep reading to arm yourself with the appropriate knowledge to streamline your business endeavors and guarantee compliance with the law.
Industrial Zoning: What Is It?
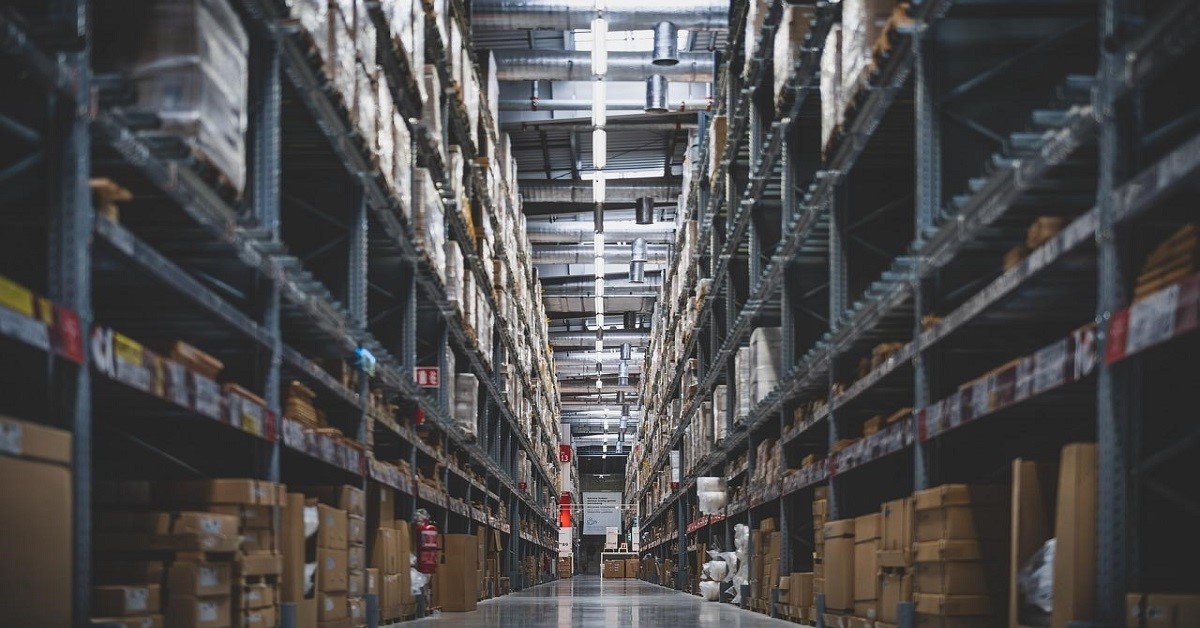
Industrial zoning refers to a defined area that sets the guidelines for constructing properties, such as factories, warehouses, and other facilities. It can distinguish residential areas from those with more intense and potentially disrupting activities. Hence, it is crucial for the development of cities worldwide.
Multiple operations are designated in the zone, including production, distribution, storage, repair, cleaning, and processing of goods and materials. Each city’s industrial zoning laws depend significantly on its unique economic needs and community goals. With this, the industry can develop without adverse impact on the local’s standard of living.
Further, it is vital to know the zoning requirements that apply depending on whether a zoned property is classified as light or heavy industrial.
Light Industrial Zoning
- Permitted Uses: This category typically includes packaging, certain manufacturing types (usually less intensive), and distribution facilities.
- Location:Light industrial zones are often closer to commercial and residential areas. This is because these activities usually generate less noise and environmental pollution compared to heavy industrial operations.
- Regulatory Focus: The regulations in light industrial zones are more lenient regarding environmental impact, allowing these areas to coexist more comfortably with non-industrial zones.
Heavy Industrial Zoning
- Permitted Uses: Heavy industrial zoning accommodates more intense industrial activities such as chemical manufacturing, mining, and power production.
- Environmental Considerations: Given the potential for significant environmental impacts, including noise pollution, smoke, odors, and waste, heavy industrial zones are subject to stricter regulations. These regulations aim to mitigate the adverse effects on the surrounding environment.
Location: Heavy industrial zones are typically located further from residential and commercial areas to minimize their impact on these communities.
Special Cases - Airports
- Classification: Airports are often categorized under heavy industrial zoning.
- Unique Regulations: They are subject to different rules and regulations due to their unique operational needs, such as the extensive land required and the additional noise from aircraft operations.
Understanding the specific zoning requirements for a given industrial activity is crucial for compliance and successful operation within the designated area.
Differences between Light and Heavy Industrial Zoning
Distribution centers, specific manufacturing types, and packaging are all permitted under light industrial zoning. Mining, chemical production, and electricity generation are examples of more intensive uses permitted by heavy industrial zoning. Because of possible drawbacks like waste, smoke, and noise pollution, rich industrial zones are typically located further away from residential and commercial areas than light industrial zones.
Restrictions on Industrial Zoning
Depending on property deeds and lender terms, industrial property development is subject to several restrictions. These could include operating hours, keeping the property in good condition, restrictions on the types of businesses allowed (like banning businesses related to alcohol or tobacco), and occupancy requirements. Restrictive covenants are another tool that landlords can use to control business hours.
Benefits of Industrial Property Zoning
Benefits of industrial zoning include enhanced safety, more usable space, and operational efficiency. Features that maximize usable square footage and improve safety and efficiency during loading operations include wider bay spacing near loading docks. The kinds of activities allowed are determined by the differences in industrial zoning regulations between light and heavy industrial zoning. Certain business types may be subject to additional restrictions imposed by retail zoning.
Potential Risks Associated with Industrial Property Zoning
Environmental hazards associated with industrial zoning include waste, smoke, noise pollution, and odors, especially in heavy industrial zones. While chemical manufacturing and mining operations are permitted in heavy industrial zones, less intensive activities like packaging and distribution are usually allowed in light industrial zones. Because of their specific land requirements and noise levels, airports are classified as heavy industrial properties subject to special regulations.
Contact Us
Thank you for your message. It has been sent.
Latest Posts
Social Profiles















