What Is Perimeter Security? Smart drone Security Solutions

Public safety and security are no mean feat; it’s a collective effort to maintain protection from risks and threats, most especially in places where people and valuable property are present. Thus, it is crucial to discover what is perimeter security.
Perimeter security definition starts with the correct systems, the necessary technologies, and the appropriate processes that can be established in order to protect the outer boundary of an area. Whether it’s a facility, site, or network, perimeter security is highly advocated as it’s a critical first line of defense.
A security perimeter is built to not only protect people, but also the attached assets and operations within the area from any external threats. The purpose of this particular controlled protection is to be proactive in deterring intrusions and detecting suspicious activity.
Though perimeter security did not start with advanced technology, it evolved from traditional physical barriers like formidable walls or security guards. Perimeter security then expanded to electronic sensors, command-integrated cameras, and even modern security has incorporated artificial intelligence (AI).
With that, numerous firms have utilised strong perimeter security to identify any potential risks before they escalate into incidents that can disrupt operations and harm individuals. Reinforcing perimeter security can encourage organizations to be resilient and recognize how public safety and security become more significant as time passes.
What Is Perimeter Security in Physical and Cybersecurity Systems?
Mentioned above was the physical perimeter security, the traditional approach that focuses on protecting through tangible measures like gates, surveillance cameras, and on-site security personnel. Visible boundaries are put in place to signal restricted access and support accountability.
As threats expand digitally, so should perimeter security. Cyber perimeter security and network perimeter security are established to defend digital environments and cyberspaces through firewalls and secure gateways, ensuring that all stored data is protected within the cyber perimeter.
Both the physical and digital perimeters have their respective definitions; the key difference between them is the following:
|
What They Protect |
How They Operate |
|
|
Physical Perimeter Security |
Property, Network, Facility, or any physical location |
Controls access to areas and assets through visible and tangible barriers |
|
Cyber Perimeter Security & Network Perimeter Security |
Data, systems, and digital resources |
Software and network controls via firewall, etc. |
Modern firms with both physical and digital spaces often use the two together, as security strategies work best when integrated with physical and digital perimeters. Coordinated systems that apply physical perimeter security, and cyber and network perimeter security can build security ecosystems that adapt to modern threats.
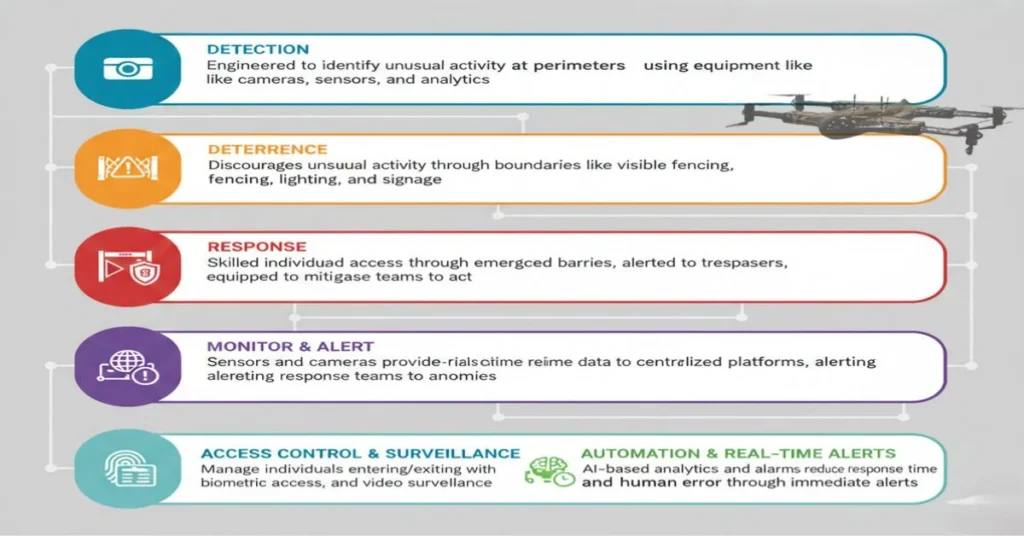
How Does Perimeter Security Work?
Modern perimeter security systems are capable of combining physical barriers with electronic sensors and response protocols to create a cohesive defense strategy. Furthermore, perimeter security systems are able to work through the following:
Detection:
This particular model is engineered to identify unusual activity at the perimeters by using equipment like cameras, sensors, and even analytics.
Deterrence:
In addition, the deterrence model is able to discourage unusual activity through boundaries like visible fencing, lighting, and signage.
Delay:
Mechanisms are also built to slow unauthorized access through reinforced barriers. This can delay any suspecting individuals long enough for response teams to act and arrive on scene.
Response:
With response teams, these are individuals skilled in managing emergencies and critical situations. In the case of detecting trespassers, they are alerted and are equipped to mitigate damage pertaining to assets or personnel.
Additionally, perimeter security also applies mechanisms that can monitor and alert. Modern perimeter security systems are included with sensors and cameras that provide real-time data to the centralized platforms, which can greatly assist any response team by alerting them when anomalies occur.
Furthermore, effective perimeter security is also integrated with access control and surveillance, wherein personnel are able to manage individuals who can enter and exit the protected areas. This involves badge systems, biometric access, and basic video surveillance altogether to verify guest identification.
Lastly, perimeter security can efficiently work in modern times through automation and real-time alerts. With AI-based analytics and alarms, it reduces response time and human error through real-time alerts for immediate action.
What Are the Key Components of Perimeter Security Systems?
A perimeter security system relies on multiple, integrated layers that work together to detect threats early and support rapid response. To achieve optimal protection, consider the perimeter security components such as:
Fencing, Walls, and Physical Barriers:
Starting with tangible measures that can be fencing, walls, and reinforced gates, this foundation is present in most perimeter security systems. Its primary purpose is to restrict unauthorized access and delay intruders upon entering the area.
Surveillance Cameras and Video Analytics:
Perimeter protection systems also use surveillance cameras and video analytics, which offer continuous visibility across all areas. This allows simple recording and video analytics to help response teams in detecting unusual behavior.
Motion Sensors and Intrusion Detection:
This particular technology is able to recognize movement or disturbances within the perimeter as it includes infrared sensors and ground-based radar. Personnel is able to detect any potential risks or issues early by using motion sensors and intrusion detection.
Access Control Points:
Individuals have to enter perimeters by using gates, badges, and, in some cases, biometrics, which are known as access control points. Perimeter security can function better with integrated access control.
Alarm and Response Systems:
As mentioned above, alarm and other response systems tie all perimeter elements together. This perimeter security system alarms trigger alerts to response and security teams, ensuring that the areas are protected and are blocked from any unauthorized runway access.
What Are the Different Types of Perimeter Security?
Other than perimeter security components, it’s also vital to understand the specific kind of perimeter security that can protect particular assets, people, and data. Here are the different types of perimeter security:
External Perimeter Security:
A type of perimeter security that focuses on protecting the outermost boundary of a location, acting as the first line of defense against threats and risks. External perimeter security includes fences, walls, and gates, which are designed to deter, detect, and delay any intruders before they reach critical areas.
Internal and Restricted-Area Perimeters:
When it comes to places within the site, internal and restricted-area perimeters are a type that must be considered. Internal perimeter security is built to safeguard sensitive zones, and restricted-area perimeters are able to control access to high-value areas; overall limiting movement once individuals have entered the site legitimately.
Virtual and Network Perimeter Security:
Digital spaces also need protection, and thus, firms can utilize virtual and network perimeter security. This specific type of perimeter security can fully protect systems, data, and communication through any, like firewalls and access controls.
Layered and Hybrid Perimeter Security:
Combining the external, internal, and virtual perimeters results in the layered and hybrid perimeter security. A unified defense strategy integrated the physical and digital controls, enabling resilience within layers of security.
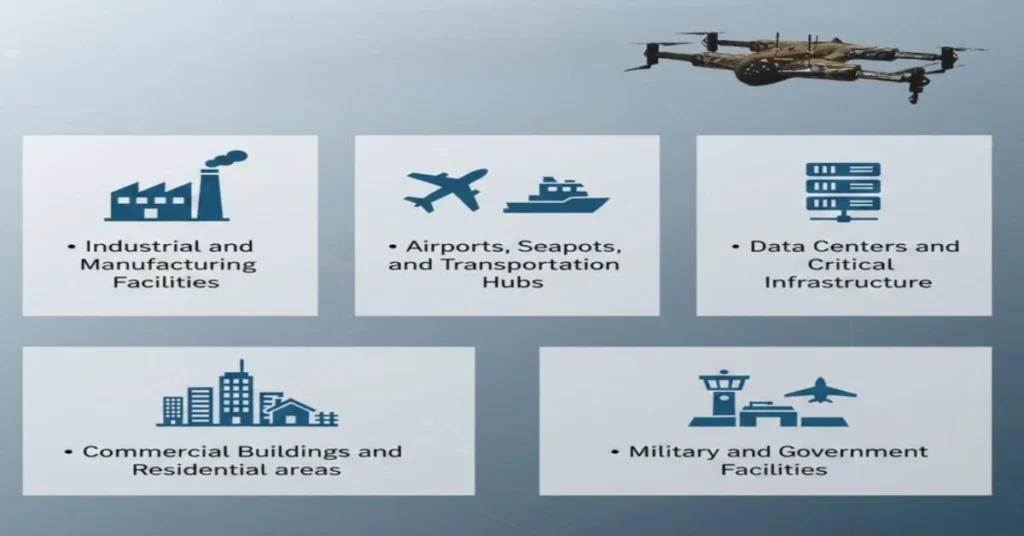
Where Is Perimeter Security Commonly Used?
Learning about the key components and the different types of perimeter security enables firms to properly assess and utilise the necessary measures to safeguard the environment, whether physical and digital. With that, it’s imperative to also understand where perimeter security is commonly used
Perimeter security cases vary, and can be easily applied by locations and industries such as:
Industrial and Manufacturing Facilities:
With numerous pieces of equipment and intellectual property, perimeter security is highly recommended in order to control access before threats reach production zones. Layered defenses ensure smooth operation while maintaining protection in the facilities and are compliant with safety regulations.
Airports, Seaports, and Transportation Hubs:
Perimeter security applications can also be utilised in airports, seaports, and any other transportation hubs. The high public traffic and critical infrastructure exposures need the necessary perimeter security that can enable efficient movement while separating secure operation zones from public areas.
Data Centers and Critical Infrastructure:
Industries with both physical and digital distributions especially require perimeter protection, as it can provide data integrity and service reliability. Physical boundaries that support digital resilience remain a foundational layer that is optimal for modern perimeter security strategies.
Commercial Buildings and Residential areas:
Accessibility and enhanced safety are also offered by perimeter security for commercial buildings and residential environments. It can deter crime, protect the occupants, and also create a sense of safety within the community, enabling adaptable solutions to become an alternative for people-centered safeguard.
Military and Government Facilities:
This represents the highest-stakes perimeter security applications, wherein breaches in military and government facilities can have national consequences. Recognizing the significance of its safety, perimeter security can have absolute control and rapid threat neutralization inside and outside sites.
What Are the Benefits of Perimeter Security?
Discovering perimeter security and its importance opens opportunities that can improve safety and protection for physical locations and digital environments. This modern era allows that and more with these perimeter security benefits:
- Early Threat Detection and Prevention: As mentioned above, early threat detection and prevention are a critical benefit since it recognizes suspicious behavior at the perimeter. Firms can gain time to respond before any assets and individuals are harmed or threatened.
- Reduced Unauthorized Access: In addition to major benefits, reduced unauthorized access defines and monitors both perimeters through physical and psychological deterrence. Entry points that are controlled by personnel are built reduce losses while reinforcing accountability.
- Improved Safety and Compliance: Multiple industries operate with improved safety and compliance, which entails strict regulatory standards, along with perimeter controls. This enforces safer environments, making it applicable for any type of industry.
- Cost Savings: Another benefit is how perimeter security is cost-effective, considering it prevents offsetting years of security investment from a single incident. From fences to monitoring equipment, perimeter security can offer a better financial alternative.
- Enhanced Situational Awareness: Lastly, the enhanced situational awareness refers to the personnel or response team having better capabilities to perceive and understand their environment. Real-time visibility and perception encourage faster and smarter decisions that are most critical during incidents.
What Challenges Does Perimeter Security Face Today?
Knowing the benefits and advantages of having perimeter security, there are also circumstances where issues and challenges arise. This may pose a difficulty in handling perimeter security challenges, such as:
- False Alarms and Sensor Limitations: One of the most common issues occurs when there are false alarms and sensor limitations. Technology like motion sensors or video analytics can be triggered by other factors like animals, vegetation, and even redundant activity, which leads to alert fatigue. Perimeter sensors can be activated by such, causing unnecessary responses and reducing trust in the established system.
- Environmental and Weather Challenges: Another limitation that complicates effectiveness is the environmental and weather challenges, which involve rain, fog, snow, etc. The environment and the weather are natural and unpredictable, making harsh outdoor conditions interfere with perimeter detection systems.
- Evolving Cyber and Physical Threats: With the existence of digital spaces, the threats directed to it also evolve. Modern attackers combine the physical intrusion with digital compromise, which exposes gaps between physical and cyber defenses.
- High Installation and Maintenance Costs: In addition, the high installation and maintenance costs remain a challenge, especially for large and remote locations. There are cases where costs are no longer justified without a long-term strategy to utilise and evolve perimeter security.
- Integration Issues with Legacy Systems: Lastly, integration issues with legacy systems can limit effectiveness relating to controls and cameras. Old technology may not be seamless with modern platforms, reducing a smooth workflow and low situational awareness.
How Is Perimeter Security Evolving With Modern Technology?
Firms and organizations can be efficient and safe in terms of perimeter security through long-term planning and its evolution with modern technology. Here’s how modern perimeter security can help in recognizing that technology reshapes defense layers:
AI-Powered Video Analytics:
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) usage enforces a significance of AI-powered video analytics in which AI perimeter security systems are able to detect unusual activity and identify threats faster. This enables monitoring large distribution centers without overwhelming security teams with common issues like false alarms, resulting in improved response time and smoother operations.
Smart Sensors and IoT Integration:
Moreover, smart sensors and IoT integration also revolutionize perimeter detection as it shares data across a unified platform. This smart perimeter security enables verification of multiple data points that can improve overall accuracy and confidence in the established protection systems in both digital and physical environments.
Automation and Predictive Threat Detection:
Similar to digital protection, automation and predictive threat detection allow analysis of historical patterns and environmental data. It notifies and provides personnel information pertaining to forecasted risks before any breaches to the locations can occur.
Mobile Monitoring and Cloud-Based Security:
Using mobile devices has reached a better method with mobile monitoring and cloud-based security, considering how response teams can access and manage perimeters remotely. Security managers are able to receive alerts and even view live feeds of all available areas from anywhere, which offers work continuity even during emergencies.
Future Trends in Perimeter Protection:
Advanced perimeter security will increasingly use AI, and combine it with robotics and autonomous response mechanisms – enhancing protection and security experience for both managers and guests. This reduces manual intervention and can help firms improve safety in the long-term.
How Do You Choose the Right Perimeter Security Solution?
As stated above, perimeter security is constantly evolving, and with that, there are multiple perimeter security solutions that are appropriate for particular situations. When choosing the right perimeter security for a specific case, it’s essential to consider the existing factors:
Risk Assessment and Site Evaluation:
Every situation for each industry is different and complex, and threats and risks vary based on location, asset value, etc. Conducting a risk assessment and site evaluation helps personnel and the system identify any entry points that have gaps, the potential environmental challenges, and even response requirements – all are essential in hopes of a better foundation of perimeter security design.
Physical, Digital, or Hybrid systems:
Choosing between physical, digital, or hybrid systems can be challenging, given the respective benefits of each system. Specifically, organizations can base the system on the following:
Best Use Cases | Overall Effectiveness | |
Physical System (Fences, Gates, etc.) | Low-risk or remote sites | Basic protection |
Digital System (Video analytics, firewall, etc.) | Data centers, offices, smart facilities | Strong visibility, limited physical deterrence |
Hybrid System (Controlled physical access with digital monitoring) | Critical infrastructure, utilities, airports | Comprehensive, layered security approach |
Scalability and Future Expansion:
Moreover, scalability and future expansion is equally important with how perimeter systems can adapt along with growing facilities and changing operations. Making modular and software-based solutions allows sustainability of perimeter securities over time, ensuring that the established system remains effective in the long term.
Compliance and Regulatory Considerations:
The compliance and regulatory considerations should also be regarded as industries are obligated to meet strict safety and data protection regulations. Following this practice influences system selection and data management, making it easier for personnel to manage.
Budget and ROI Evaluation:
With cost, budget, and return on investment (ROI) evaluation, organizations must recognize how this is a long-term value. Other things to consider, as fewer incidents and operational efficiency can more than justify the investment in perimeter security, which reinforces that the right perimeter security solution is a cohesive protection strategy for any type of industry.

How Are Drones Enhancing Modern Perimeter Security?
In addition to a hybrid perimeter security system, upcoming protection measures can be further enhanced by incorporating drones and other unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs). Intelligent, mobile technology enables drone perimeter security and security drones that enhance visibility, speed, and response times.
It’s simple yet powerful, a strategy that is beyond traditional systems like fences and cameras. Here’s how drones can enhance modern perimeter security:
- Role of Drones in Perimeter Security Monitoring: Drones play an active role in perimeter security monitoring as it is built to provide on-demand and automated patrols. Personnel can consistently utilise drones for monitoring areas remotely, and can even use the live feed in detecting any unusual activity.
- Aerial Surveillance for Large and Hard-to-Secure Areas: Its aerial perimeter surveillance is able to cover large, remote, and even complex environments faster, compared to traditional methods that can take up most operating hours. This reduced response time and prevents costly damage, proving that the investment in drones for perimeter security is indeed justified and effective.
- Real-time Threat Detection and Incident Verification: Having access to areas through a security drone’s live-camera feed can help response teams in early threat detection and incident verification. Drones are automatically dispatched when alarms are triggered, visually confirming the threat and enabling informed decision-making.
- Integration of Drones with Existing Perimeter Security Systems: It is easy for personnel to seamlessly connect security drones with existing perimeter security systems, including access control, video management software, etc. Consequently, security drones become part of the security ecosystems rather than a standalone tool that needs to adjust to the system for every flight mission.
- Use of Thermal Imaging and Night Surveillance: Perimeter security improves with drones’ thermal imaging and night surveillance, which makes it easier for personnel to assess areas that lack light and can even detect heat signatures in low-visibility conditions. This feature is most appropriate for logistics hubs that operate around the clock.
- Benefits of Drone-Based Perimeter Security: Most importantly, drone-based perimeter security offers speed, flexible coverage, and scalable deployment. With security drones, response teams are able to respond to growing threats more efficiently with comprehensive situational awareness.
FAQ
How effective is perimeter security against modern threats?
Perimeter security can operate significantly when well designed, as it is built to deter, detect, and delay modern threats and breaches before their escalation.
What factors should be considered when designing a security perimeter?
Designing an effective security perimeter often involves regarding the site layout, risk level, surrounding environment, asset value, compliance requirements and regulations, and future expansion plans.
Can perimeter security reduce false alarms and security breaches?
Yes. Modern perimeter security utilizes analytics and verification to reduce false alarms while improving accuracy in detecting genuine threats, risks, and issues.
How does perimeter security adapt to large or remote locations?
Perimeter security is able to adapt by combining layered defenses, remote monitoring, and the necessary technologies like drones and UAVs to maintain coverage across large areas.
What role does automation play in perimeter security systems?
Automation plays a role in faster detection, intelligent alerts, and consistent responses. Having an automated perimeter security system improves operational efficiency.
Are perimeter security solutions scalable as facilities expand?
Most modern perimeter security solutions are modular, indicating that they can scale coverage and capabilities alongside growing sites.
How does perimeter security support real-time incident response?
Perimeter security supports response through integrated sensors, cameras, and live alerts, which provide immediate visibility that can in responding quickly and decisively.
What future trends are shaping the next generation of perimeter security?
Future trends include AI-driven analytics, autonomous drones, IoT sensors, and cloud-based platforms – all of which can transform the current state of perimeter security. They redefine methods into smarter and more adaptive perimeter security.
Contact Us
Thank you for your message. It has been sent.





